p { margin-bottom: 0.08in; }
It was a funny feeling, seeing so many faces from Occupy San Francisco and Occupy Oakland in the bright, clean “Gold Room” of San Francisco’s Commonwealth Club, particularly after spending so many nights camping with them and covering the movement.
But they were there on Dec. 15, just up Market Street from their old campsites, along with a couple hundred supporters and interested community members, attending a forum on “Occupy: What now? What’s next?” Facilitator Caroline Moriarty Sacks announced that she “expected a civic conversation.” What she got was a very Occupy answer to the question of the evening which, in typical style, redefined the very concept of “civic” conversation.
The forum involved voices from many different parts of the left. Jean Quan, the Oakland mayor with a progressive activist past. George Lakoff, an outspoken liberal professor of linguistics at UC Berkeley. In the audience, dozens of people who support or are interested in Occupy, the mostly leftist San Francisco political milieu. And, of course, representing most of the panel and a good chunk of the audience were the active occupiers: anarchists, peace activists, labor organizers, and everything in between.
During the panels, their perspectives clashed. Yet Occupy strives to be a coalition of everyone, and all of these voices will be important as it progresses. Sacks had planned a 90-minute forum, featuring a panel to answer both moderator and audience questions, a break-out session, and summary reports back.
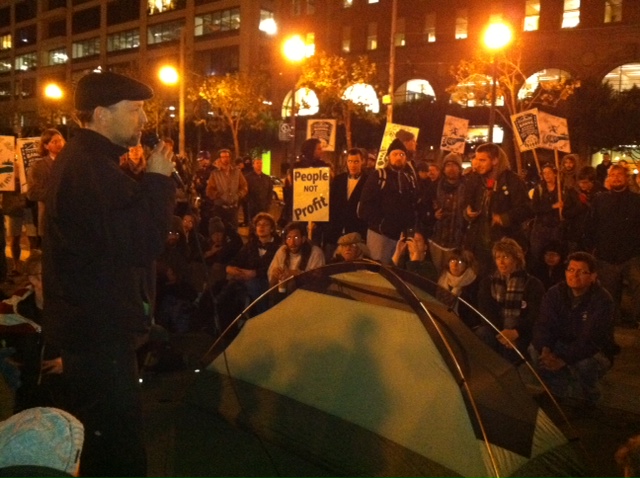
In their quest to practice participatory democracy, Occupy protesters have become used to long meetings that strive for non-hierarchical structure and a platform to hear the voice of anyone who would like to speak. If there’s one thing they can all agree upon, it’s that they’re a little tired of waiting patiently for their voices to be heard.
During the panel discussion, a few Occupiers started a Peoples Mic, interrupting Mayor Quan. They were escorted out. This fazed no one, and by the time she left the panel, chants demanding her recall rang in the hall. At each disruption, some Occupy-involved folks would object, “Listen to her! I want to hear all viewpoints!”
The tone was rowdy, but not aggressive. Minutes after disrupting the forum, protesters were back on schedule, sitting in small groups engaged in dialogue with other audience members. Even Quan was fine with it; she told the Oakland Tribune, “It was a chance to talk and have dialogue…We fostered a debate.”
This event was a microcosm of the thorny but crucial way that Occupy is uniting the left. The people in the room had something in common: belief in the visions and goals of Occupy. They just disagreed on how to get there.
Discussing, debating, and creatively bridging these differences has been one of the movement’s greatest struggles. But the more Occupy succeeds on the thorny path to unity, the more its strength builds.
Misrepresenting anarchism
Civil disobedience, peace, non-violence—all of these are critical concepts for the Occupy movement, and wrestling with them frankly has been part of the long road towards unification.
This has been done through the application of what’s originally an anarchist concept: embracing a diversity of tactics.
This is what the Occupy protesters did at the Commonwealth Club Forum. Some disapproved of disruptions, others thought them necessary. Individuals acted as they felt was right.
The Occupy supporters who turned their backs on Quan and interrupted her didn’t do it because they are inexplicably rude. They gave their reasons, including still being hurt and angry after Quan unleashed police using tear gas, rubber bullets, and aggression to break up their encampment on Oct. 25.
Quan also was displeased about that night’s events, saying that “No one is happy about what happened around the tear gas and mutual aid.”
The second reason for the reactions was what an Occupy Oakland protester who mic-checked Quan called her “misrepresentation of anarchism.” This has been dismissed and mocked by many press outlets, as if to say: What’s the point of bothering to understand anarchism?
Many people who identify with anarchist principles and tactics are involved with Occupy groups. This has contributed to the growth and development of autonomous communities at camps, as many anarchists have extensive knowledge and practice in building alternative communities based on horizontalism and collective management of resources. Occupy’s anarchist roots go deep.
This has also created controversy when tactics like property destruction and the black bloc, both associated with anarchism, become a part of Occupy. One example was the bank windows smashed and vacant building occupied during Occupy Oakland’s General Strike on Nov. 2, and riot police again responded with tear gas that night. The next day, 700 attended a General Assembly meeting to focus on discussing violence, its nature, and the ethics surrounding it.
Many have been quick to characterize this ongoing debate as a division in the movement. But if unity is to be achieved, these tough conversations are necessary.
Bringing it home
Occupy has been criticized for its lack of leaders, but that has left it open to exciting possibilities. To start a new Occupy project, you just have to convince some people to help you out—you must gain approval from no one. Some have described the organization as a “do-ocracy.” Don’t ask for permission, they say, just do it.
As such, the ideas for moving forward span from handfuls of people on street corners to millions converging on Washington.
Lakoff presented one of these concepts to the group at the Commonwealth Club, what he called “Occupy Elections.” Lakoff said, “Join Democratic clubs, and insist on supporting those people with your general moral principles. If you join Democratic clubs soon, you decide who gets to run. This is how the Tea Party took over.”
Like most ideas floating around in Occupy, there’s already something similar underway. Berkeley resident Joshua Green started the Occupy the Congress initiative, which hopes to organize and fund efforts for candidates “who support the declaration of the occupation of Wall Street.” Congressional candidates such as Elizabeth Warren in Massachusetts and Norman Solomon here in California have expressed support for and goals similar to the Occupy movement.
Occupy Washington DC has taken the message to Congress in other ways. In an open forum with supporters and renowned economists, they developed their Budget Proposal for the 99 Percent and are coordinating with Occupy groups throughout the country to call for a National Occupation of Washington DC starting March 30.
A call to action like that has a chance of being huge. With the West Coast Port Shutdown on Dec. 12, Occupy has demonstrated an ability to coordinate nationally. Those actions also showed Occupy’s growing unity with labor groups, as ILWU members worked closely with Occupy to plan those actions.
On Dec. 6, Occupy demonstrated its dedication to yet another new frontier—occupying foreclosed homes. That was a national day of action called by Occupy Our Homes and Occupy groups in over two dozen cities participated, defending homeowners threatened with eviction and moving the homeless into empty properties.
Hibernation
By the time moderator Melissa Griffin asked her final question to the panel, it was clear that the “civic conversation” had not gone as planned. Two Occupy protesters had been escorted out for interrupting Jean Quan. A handful of others had stood and turned their backs when she spoke. The crowd was restless for their own chance to grill the panelists, and there were only a few minutes left. With a faint look of dismay and hopelessness, Griffin asked the question that had no chance of being quickly answered: What’s next for occupy?
She quoted Kalle Lasn, co-founder of Adbusters, the “culture-jamming” organization credited with prompting Occupy Wall Street. In a recent interview with NPR, Lasn said: “I think that we should hibernate for the winter. We should brainstorm with each other. We should network with each other and then come out swinging next spring.” Griffin asked the panelists if they agreed with that statement.
Of course, some did and some didn’t. In fact, some form of “hibernation” is what many plan to do. In San Francisco, Occupy reading groups, workshops, and educational circles are on the rise. Small actions happen almost daily, ranging from workshops to meetings to marches to pop-up occupations.
Occupiers who were kicked out of camps are sleeping in networks of squats, safe-houses, and what one long-time camper described as “little homeless encampments around the city. We don’t put up an Occupy banner, and police don’t arrest us.”
The forum was a microcosm of the debates and plans brewing within Occupy, and it ended like most Occupy events. New connections had been made. Most people trickled out while several Occupy campers stayed to help stack chairs and clean up from the event. They all eventually exited the warm building, with its empty lobby that could have slept at least 50 people. OccupySF and Oakland activists chatted and advised each other on where to go.
Occupy is a resurgence in the spirit and power of protest and peoples movements, a recognition that the personal is political, that individuals losing their jobs and their homes can have more power in numbers. Organizing and protest has become a lifestyle.
As the Occupiers left the Commonwealth Club building, the future seemed thrilling, although many still needed a place to sleep for the night while those possibilities continue to percolate.